What Is Zero-knowledge Storage? (and Why Your App Needs It)
Understanding Zero-Knowledge Cloud Storage
Cloud storage is everywhere, but not all cloud providers treat your data the same way. While traditional services like Google Drive, Dropbox, or OneDrive offer convenience, they also come with a major security trade-off: they can access your files. That’s where zero-knowledge cloud storage changes the game.
Unlike traditional cloud storage, zero-knowledge encryption ensures that only you, not even the service provider, can access your data. This approach eliminates third-party access risks, making it an essential choice for applications handling sensitive information or requiring GDPR-compliant storage.
What Does “Zero-Knowledge” Mean in Data Storage?
The term zero-knowledge in cloud storage refers to a system where the provider has no knowledge of your stored data. This is possible through end-to-end encryption (E2EE), a security model that ensures data is encrypted before it leaves your device and can only be decrypted by you.
How it works:
- Encryption Happens Locally: Before your file is uploaded to the cloud, it is encrypted on your device using a unique key that only you control.
- Cloud Servers Store Encrypted Data: The storage provider never sees the raw file, only an encrypted version of it.
- Decryption Happens Only on Your Device: When you access the file, your private key decrypts it locally, meaning the cloud provider never has access to the actual content.
This system ensures that your files are completely private, even from the company hosting them.
How Zero-Knowledge Storage Differs from Traditional Cloud Storage
Most mainstream cloud providers like Google Drive, Dropbox, and OneDrive use server-side encryption, meaning they encrypt your data but also hold the keys to decrypt it. This allows them to:
- ✔ Scan your files for metadata and indexing
- ✔ Use AI to analyze content for ads and recommendations
- ✔ Comply with data access requests from governments or third parties
While this makes file retrieval and search faster, it also means your data isn’t truly private. The cloud provider could potentially read, modify, or share your files if required.
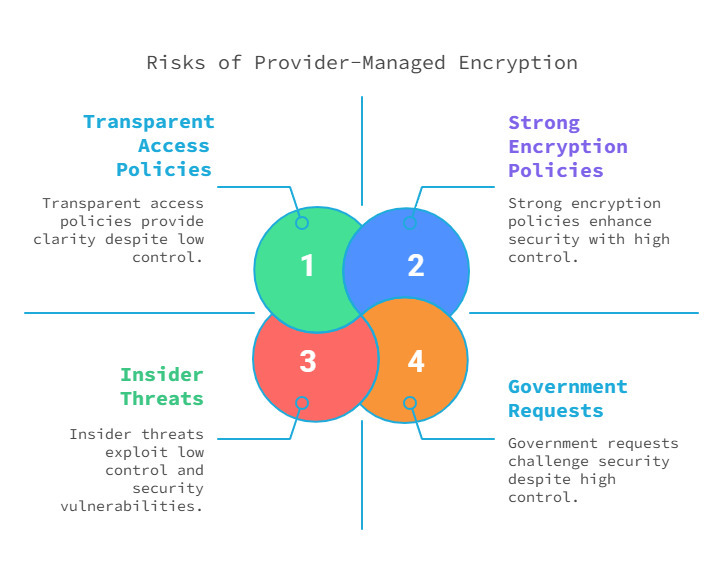
Why Server-Side Encryption Isn’t Enough
Many services claim to offer “secure cloud storage” because they encrypt data at rest (while stored) and in transit (while being sent to the cloud). However, the encryption keys are managed by the provider, meaning:
- The provider can decrypt your data at any time.
- A data breach or insider attack could expose your files.
- Governments and third parties can request access to your stored information.
With zero-knowledge encryption, these risks are eliminated. Only you hold the decryption key, making it impossible for anyone else, even the storage provider, to access your files.
This is why zero-knowledge cloud storage is essential for privacy-focused applications and why businesses handling sensitive data must consider GDPR-compliant storage solutions to protect their users.
Why Zero-Knowledge Storage Matters for Security & Compliance
Data privacy laws are becoming stricter, and organizations must ensure that their cloud storage solutions comply with regulations like GDPR and HIPAA. Traditional cloud providers store files in an encrypted format but still retain access to encryption keys, creating potential security and compliance risks.
Zero-knowledge storage eliminates these risks by ensuring that only the user can decrypt their data, making it an essential solution for businesses that handle sensitive user information, healthcare records, or personal data protected by law.
The Role of Zero-Knowledge Storage in GDPR Compliance
The General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) sets strict rules on how organizations collect, store, and process user data. One of its key principles is data minimization, which means companies should only store what is necessary and ensure maximum privacy by design.
Zero-knowledge encryption aligns with GDPR in several ways:
- True Data Ownership: Since only users have access to their encryption keys, businesses cannot access or process personal data without user consent, reducing compliance risks.
- Encryption at Rest and in Transit: GDPR requires organizations to use strong encryption to protect data from breaches. Zero-knowledge storage encrypts files before upload, ensuring that no readable data is ever exposed, even if a cloud provider is hacked.
- The Right to Be Forgotten: GDPR allows users to request the deletion of their personal data. With zero-knowledge encryption, businesses can simply delete the encryption key, making the data permanently inaccessible.
Companies that store customer data, payment records, or sensitive business documents should adopt zero-knowledge storage to meet GDPR requirements while protecting user privacy.
Meeting HIPAA Standards with End-to-End Encryption
In the healthcare industry, Protected Health Information (PHI) must be stored securely to comply with the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA). A data breach involving PHI can result in severe financial penalties and legal consequences.
Zero-knowledge storage plays a critical role in HIPAA compliance by ensuring:
- End-to-End Encryption for PHI: Medical records, lab results, and patient histories are encrypted before being stored, preventing unauthorized access.
- Access Control Mechanisms: HIPAA requires strict role-based access control (RBAC), ensuring that only authorized personnel can view or modify patient data. With zero-knowledge storage, even IT administrators cannot access files without explicit authorization.
- Data Minimization: Storing only the necessary patient data and encrypting it at the source ensures compliance with HIPAA’s privacy and security rules.
Healthcare providers, medical research firms, and insurance companies should consider zero-knowledge storage as a core part of their data protection strategy to avoid compliance risks and safeguard patient privacy.
Key Benefits of Zero-Knowledge Cloud Storage
Zero-knowledge cloud storage offers more than just compliance with regulations like GDPR and HIPAA. It provides a level of privacy, security, and control that traditional cloud providers cannot match. By ensuring that only the user can access their files, this approach eliminates common risks associated with centralized data storage and third-party access.
No Third-Party Access to Your Data
One of the most significant advantages of zero-knowledge storage is that not even the cloud provider can decrypt or access your data. Unlike traditional cloud services, where providers manage encryption keys and can technically read, scan, or share your files, zero-knowledge encryption ensures that only you hold the keys.
This level of privacy is critical for:
- Businesses handling confidential client data who cannot risk third-party exposure.
- Individuals concerned about government surveillance or unauthorized access.
- Organizations storing financial, legal, or intellectual property documents that must remain strictly private.
By removing the provider’s ability to access stored data, zero-knowledge storage eliminates trust-based security models and ensures true data ownership.
Protection Against Data Breaches & Insider Threats
Even the most secure cloud providers can experience security breaches or internal threats, leading to data leaks, ransomware attacks, or unauthorized access. Since traditional cloud storage relies on provider-controlled encryption keys, any compromise in the provider’s security could expose all user data.
Zero-knowledge encryption mitigates these risks because:
- Even if a cloud provider is hacked, the attackers cannot decrypt stolen data.
- Malicious insiders within a cloud company have no way to access private user files.
- Data is useless without the user’s unique encryption key, adding an extra layer of protection.
For businesses that store sensitive customer records, legal contracts, or financial data, zero-knowledge storage provides an unmatched level of resilience against cybersecurity threats.
Full User Control Over Encryption Keys
In most cloud services, users rely on the provider to manage encryption keys, which creates a single point of failure. If the provider’s security is compromised or if they receive a government request, user data can be accessed without consent.
Zero-knowledge storage ensures that encryption keys remain in the hands of the user, offering:
- Complete privacy since no third party can access or decrypt files.
- Protection against unauthorized disclosures, even under legal pressure.
- Greater control over data management and access permissions.
This approach is essential for organizations and individuals who prioritize privacy and control, ensuring that their files remain secure without external dependencies.
How ByteHide Storage Provides GDPR-Compliant Zero-Knowledge Security
Storing sensitive data in the cloud comes with significant security and compliance challenges. Traditional cloud providers like Google Drive and Dropbox encrypt user files, but they retain control over encryption keys, meaning they can access, scan, or share stored information if needed. This creates compliance risks for businesses handling personal data, healthcare records, or confidential documents under GDPR and HIPAA regulations.
ByteHide Storage eliminates these risks by offering true zero-knowledge encryption and built-in compliance features. Unlike mainstream providers, ByteHide ensures that only users have access to their data, making it a fully private and regulation-ready cloud storage solution.
True End-to-End Encryption with ByteHide
One of the biggest differences between ByteHide Storage and traditional cloud providers is how encryption is handled. Many popular services encrypt files only after they reach the cloud, meaning that the provider has access to both the encrypted files and the decryption keys. This allows them to:
- ✔ Analyze and index files for metadata and recommendations
- ✔ Scan documents for policy enforcement or advertising purposes
- ✔ Provide access to files if requested by governments or third parties
ByteHide Storage takes a fundamentally different approach by implementing true end-to-end encryption (E2EE). This means:
- Data is encrypted before leaving the user’s device. The encryption process happens locally, ensuring that raw data is never exposed to ByteHide or any third party.
- Decryption is possible only on the user’s side. Even if someone intercepts the files in transit or gains access to ByteHide’s servers, they cannot decrypt the data without the user’s key.
- No master encryption key is stored on the cloud. Unlike traditional providers, ByteHide does not retain decryption keys, eliminating any risk of unauthorized access.
Comparison with Google Drive & Dropbox Encryption
With ByteHide’s zero-knowledge approach, even in the event of a data breach or legal request, no one except the user can access their stored files. This ensures that sensitive business documents, personal records, and regulated data remain fully protected at all times.
Automated Compliance for GDPR and HIPAA
Handling data compliance manually can be time-consuming and prone to errors. Businesses that store customer data, healthcare records, or financial documents must meet strict regulatory requirements, including data retention policies, audit trails, and controlled access management. ByteHide Storage automates these processes to ensure seamless compliance with GDPR and HIPAA.
Built-in Data Retention Policies & Audit Trails
- Automatic Retention Management: Businesses can set custom data retention policies to automatically delete stored files after a specified period, helping comply with GDPR’s “right to be forgotten” and HIPAA’s data retention mandates.
- Tamper-Proof Audit Logs: ByteHide provides detailed audit trails that track file access, modifications, and deletions. This ensures full transparency and compliance with data protection authorities.
Secure Role-Based Access Control (RBAC) for Managing Permissions
Managing who can access stored files is critical for security and compliance. ByteHide Storage integrates Role-Based Access Control (RBAC), allowing organizations to:
- Define granular permissions for different user roles, ensuring that only authorized personnel can view or modify files.
- Enforce least-privilege access policies, minimizing the risk of accidental or malicious data exposure.
- Restrict access to sensitive data based on user roles, device authentication, or predefined security rules.
ByteHide’s automated compliance features help businesses eliminate manual security risks, ensuring that they meet regulatory requirements while keeping their data fully private and under control.
Choosing the Right Zero-Knowledge Storage for Your App
Not all cloud storage solutions offer the same level of privacy and security. While many providers claim to encrypt data, only zero-knowledge storage guarantees that no one but the user has access to their files. For applications handling sensitive information, choosing the right provider is essential to ensure compliance, security, and seamless integration.
Key Features to Look for in a Secure Cloud Provider
When evaluating a zero-knowledge cloud storage provider, consider the following must-have security features:
-
Zero-Knowledge Encryption
- The most important feature is end-to-end encryption (E2EE), where files are encrypted before leaving the user’s device and can only be decrypted by them. This ensures that even if the cloud provider is compromised, no one can access the stored data.
-
AES-256 Encryption for Maximum Security
- Look for a provider that uses AES-256 encryption, the same standard used by governments and financial institutions. AES-256 is virtually unbreakable, providing strong protection against brute-force attacks.
-
Zero-Trust Authentication
- A zero-trust model ensures that every access request is strictly verified, even from internal systems. This prevents unauthorized access and reduces the risk of insider threats.
-
Decentralized or Distributed Storage Options
- Some zero-knowledge providers use decentralized storage to enhance security and redundancy. Instead of storing data in a single centralized location, files are split and distributed across multiple nodes, making breaches significantly harder.
-
Compliance with GDPR & HIPAA
- If your app handles personal or healthcare data, ensure the provider has built-in compliance tools for data retention policies, access control, and audit logs.
-
Granular Access Controls
- Role-based access control (RBAC) is crucial to limit who can view or modify specific files. Look for solutions that allow fine-grained permissions based on roles, device authentication, or geographic restrictions.
By prioritizing these features, you can ensure that your application’s storage is not only secure but also scalable and compliant with data protection regulations.
How to Migrate to Zero-Knowledge Storage Without Disruptions
Transitioning from a traditional cloud provider to a zero-knowledge storage solution can seem complex, but following a structured migration plan ensures a smooth and disruption-free process.
Step 1: Assess Your Current Storage Setup
- Identify where your files are currently stored (Google Drive, AWS S3, Dropbox, etc.).
- Review encryption policies, access controls, and compliance gaps.
- Determine which files need to be migrated first, prioritizing sensitive or regulated data.
Step 2: Choose the Right Zero-Knowledge Provider
- Select a provider that offers end-to-end encryption, compliance tools, and API support.
- Ensure SDKs and integrations are available for your tech stack to avoid compatibility issues.
Step 3: Encrypt Data Before Migration
- If your current provider does not use zero-knowledge encryption, encrypt sensitive files before transferring them.
- Use a local encryption tool or work with the new provider to automate pre-migration encryption.
Step 4: Gradual Migration & Testing
- Start by migrating non-critical files to test performance and compatibility.
- Implement a dual-storage model where old and new providers run in parallel to minimize downtime.
- Test access controls, decryption processes, and API calls to ensure functionality remains intact.
Step 5: Final Cutover & Optimization
- Once testing is complete, fully switch to the zero-knowledge storage provider.
- Remove old storage locations to prevent accidental data exposure.
- Optimize backup strategies, access policies, and automated compliance workflows.
Future-Proofing Your App with Zero-Knowledge Storage
The way businesses handle data security and privacy is changing. With growing concerns about data breaches, government surveillance, and compliance regulations, traditional cloud storage is no longer enough to protect sensitive information.
Why Traditional Cloud Storage Falls Short
Popular providers like Google Drive and Dropbox offer encryption, but since they control the encryption keys, they can access, scan, or share your files if required. This introduces serious privacy risks and makes compliance with regulations like GDPR and HIPAA more difficult.
The Growing Demand for Privacy-First Applications
Users and businesses are demanding better data security. With the rise of GDPR, HIPAA, and other global privacy laws, organizations must prioritize encryption, data control, and compliance.
Zero-knowledge storage is becoming the standard for privacy-first applications because it:
- ✔ Ensures only the user can access their data with true end-to-end encryption.
- ✔ Eliminates the risk of third-party exposure or government data requests.
- ✔ Helps companies achieve compliance effortlessly with built-in security policies.
How ByteHide Storage Simplifies Security & Compliance
ByteHide Storage is designed to make zero-knowledge security accessible and easy to implement. Unlike traditional storage solutions, ByteHide ensures that:
- All data is encrypted before leaving the user’s device, making it impossible for third parties to access.
- Zero-trust authentication and role-based access control (RBAC) protect files from unauthorized access.
- Automated compliance tools help businesses meet GDPR, HIPAA, and SOC 2 requirements without extra effort.
By integrating ByteHide Storage, developers can future-proof their applications, ensuring that user data remains secure, private, and compliant without sacrificing performance or ease of use.
The shift toward zero-knowledge cloud storage is happening now. Choosing the right storage solution today means stronger security, easier compliance, and greater trust from users in the long run.
Popular Products
-
 Car Interior Disassembly Kit
Car Interior Disassembly Kit$81.99$56.78 -
 Car Fire Extinguisher Storage Bag
Car Fire Extinguisher Storage Bag$49.99$25.00 -
 Brushless Cordless Oscillating Multi-...
Brushless Cordless Oscillating Multi-...$1,453.99$869.78 -
 Waterproof Trauma Medical First Aid Kit
Waterproof Trauma Medical First Aid Kit$121.99$84.78 -
 All-Purpose First Aid Kit for Home & ...
All-Purpose First Aid Kit for Home & ...$144.99$100.78